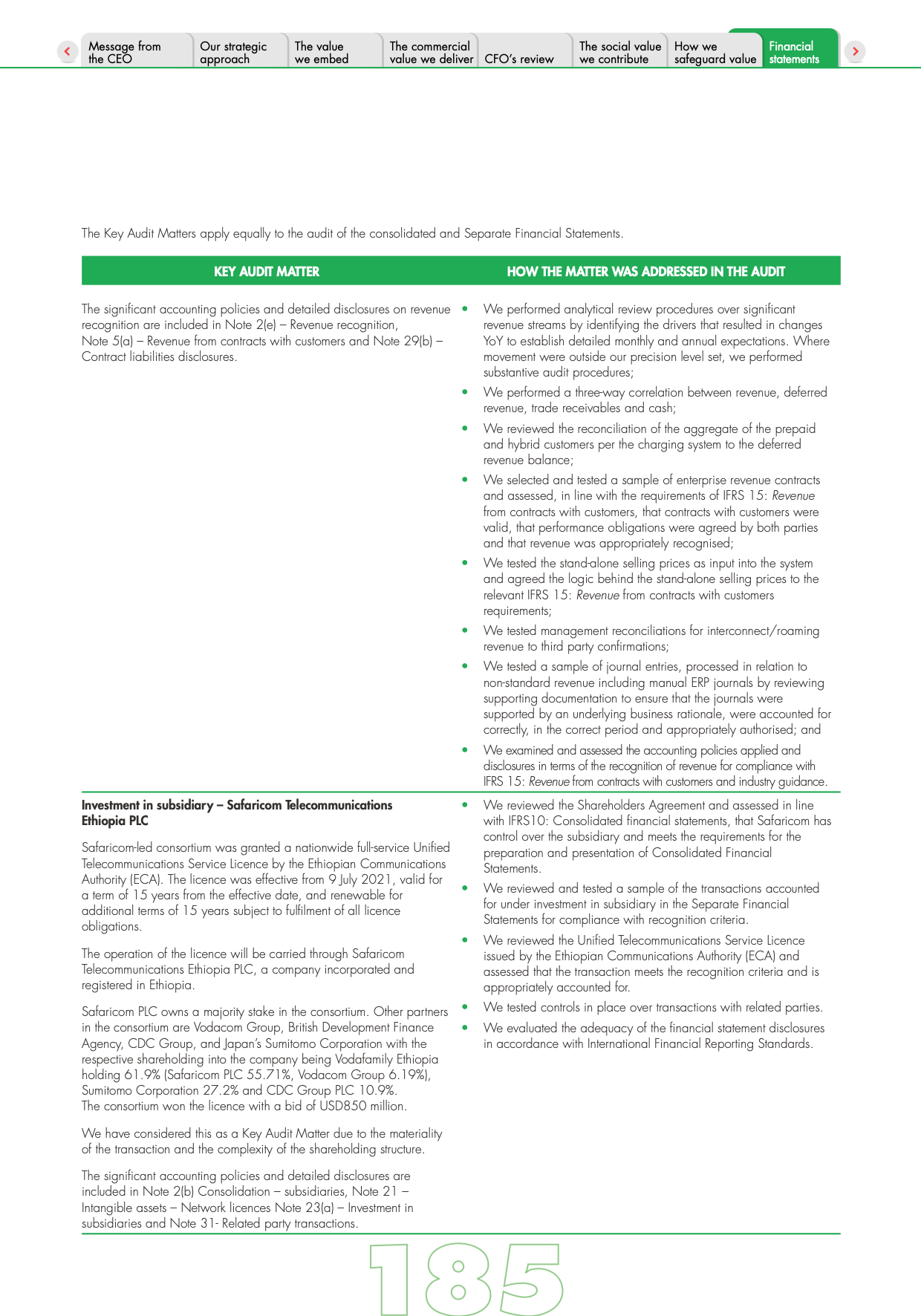
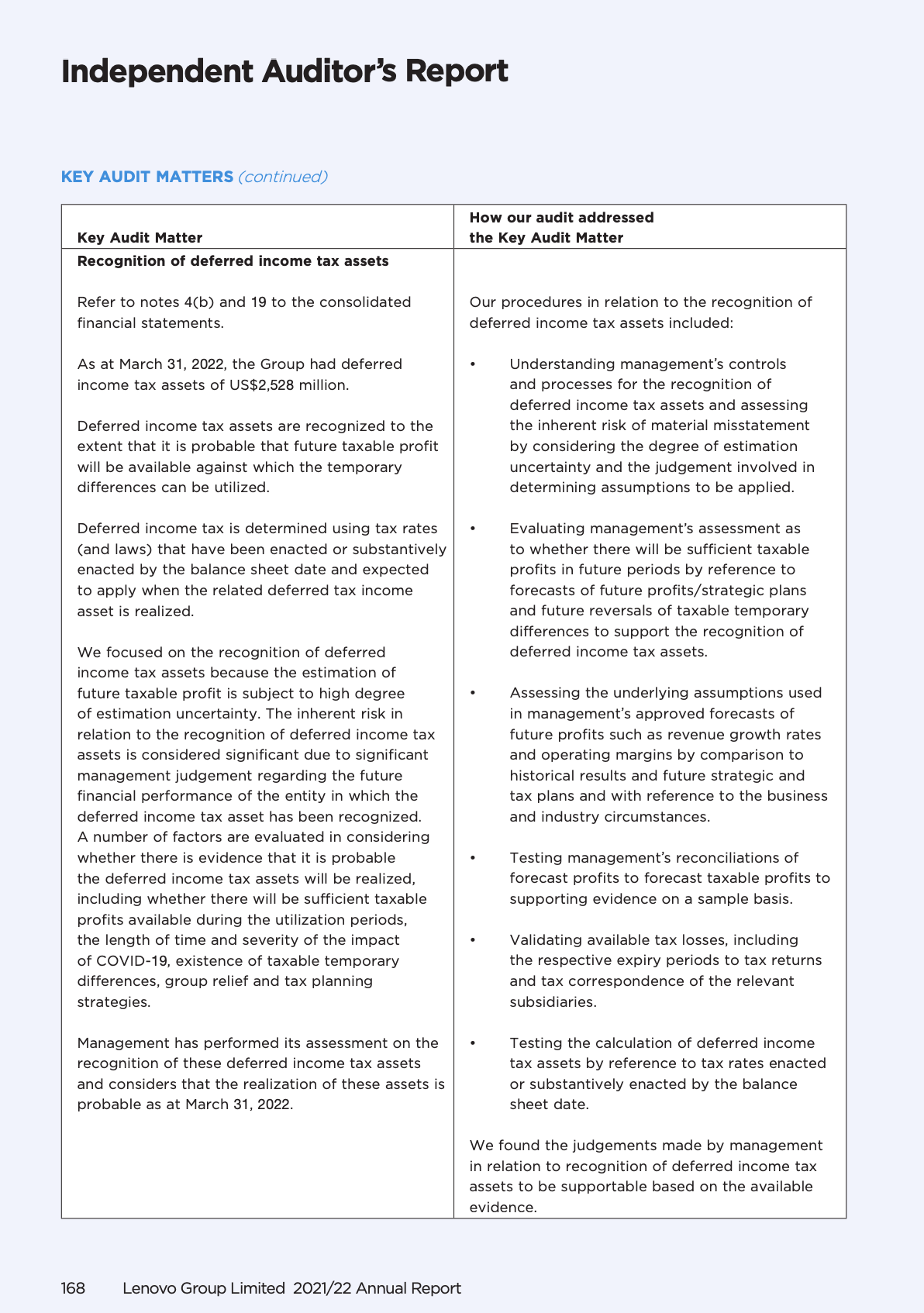
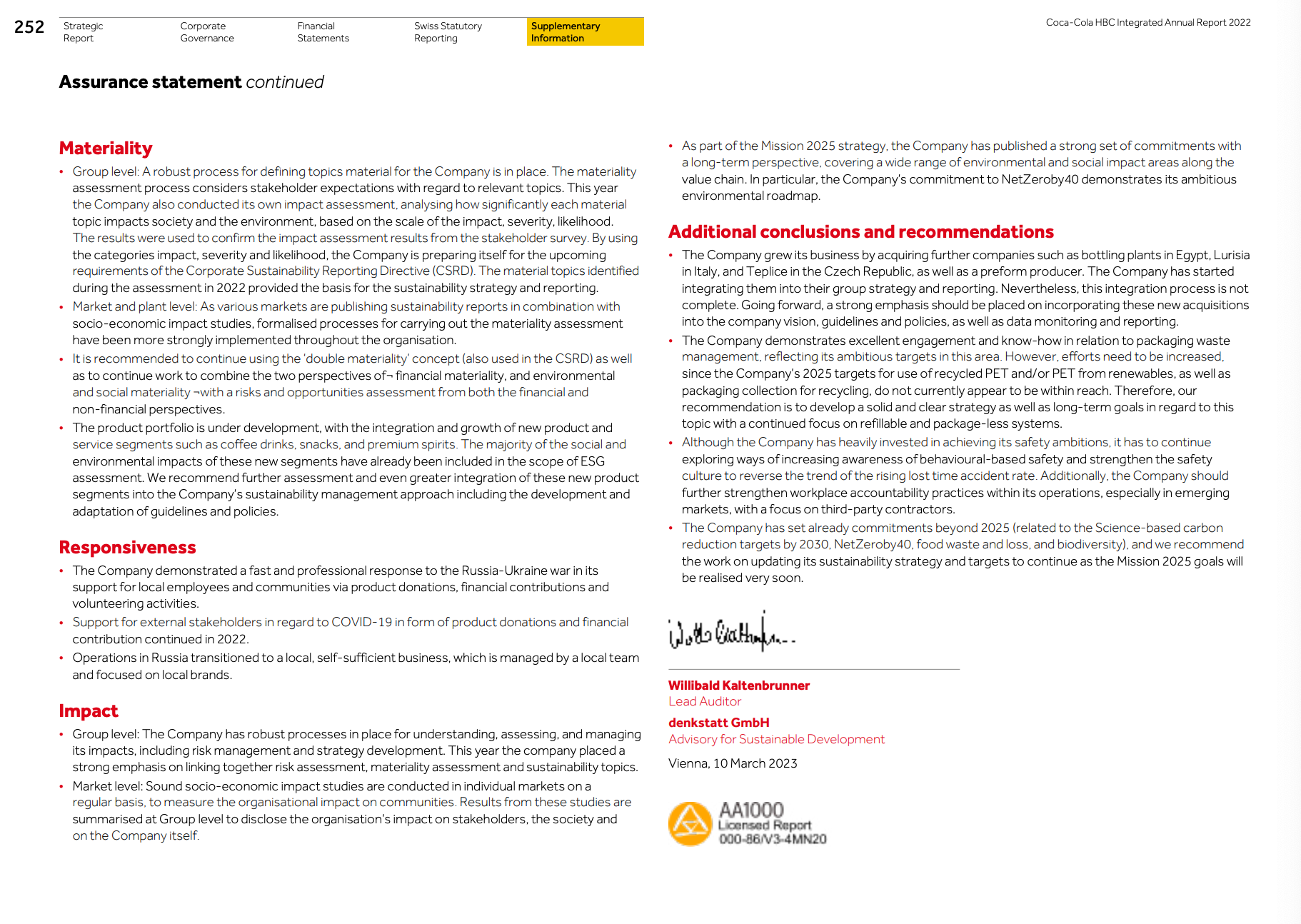
The financial statements should be accompanied by an independent auditor’s report. The auditor’s report should include an affirmation that the financial statements have been prepared by management and audited by an independent, qualified, and competent auditor.
The auditor’s report should also include an audit opinion as to whether financial statements are prepared, in all material respects, in accordance with the applicable financial reporting framework. There are four types of audit opinion:
- An unqualified opinion indicates that the financial statements fairly reflect the client’s financial results and financial position;
- A qualified opinion indicates limitations in the scope of the audit and that certain information could not be verified;
- An adverse opinion indicates significant issues with the financial statements, including possible material misstatements or irregularities;
- A disclaimer opinion indicates that no opinion can be given due to lack of sufficient financial records and information.
Larger and publicly listed companies are expected to have their financial statements audited according to international auditing standards, such as the International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS), International Standards on Auditing (ISA) by the International Auditing and Assurance Standards Board, and other generally accepted international best practices such as the Financial Accounting Standards Board Generally Accepted Auditing Standards (GAAS).
Companies are increasingly expected to provide assurance of sustainability information.
Audit of Financial Information
The annual report should include an audit opinion – and affirmation that financial statements have been prepared by management and audited by an independent, qualified, and competent auditor.
Larger and publicly listed companies are expected to follow international auditing standards, such as International Standards on Auditing (ISA) and Generally Accepted Auditing Standards (GAAS).
Resources
This ISA standard deals with the auditor’s responsibility to form an opinion (Qualified, Adverse, or Disclaimer of Opinion) on the financial statements and the form and content of the auditor’s report issued as a result of an audit of financial statements.
Sustainability Assurance
Companies are increasingly expected to provide assurance attestations that sustainability information is reliable for internal management and external reporting.
An assurance attestation is a review by an independent accountant of management’s assertion that the sustainability information in the annual report is presented in accordance with sustainability accounting or reporting standards such as the International Standard on Assurance Engagements ISAE 3000 (Revised), Assurance Engagements Other than Audits or Reviews of Historical Financial Information, International Framework for Assurance Engagements, and Related Conforming Amendments, the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) or the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board Standards (SASB).
This requires the company to clearly establish the data’s scope, definition, and internal collection process. Assurance attestation engagements can be done either on a reasonable or a limited basis.
Reasonable assurance: exists when an independent party measures or evaluates the underlying subject matter against the criteria.
Limited assurance: exists when practitioner measures or evaluates the underlying subject matter against the criteria.
Emerging Standards for Sustainability Assurance
The International Auditing and Assurance Standards Board (IAASB) recently issued guidance for assurance for nonfinancial reporting, including sustainability or ESG reporting. The guidance builds upon International Standard on Assurance Engagements ISAE 3000 (Revised), Assurance Engagements Other than Audits or Reviews of Historical Financial Information, International Framework for Assurance Engagements, and Related Conforming Amendments and applies it to extended external reporting assurance engagements.
The revised ISAE provides requirements and guidance on assurance engagements, including reasonable and limited assurance attestation engagements.
Other relevant standards include ISAE 3410, Assurance Engagements on Greenhouse Gas Statements, which provides requirements and guidance specific to engagements on GHG Statements.
Oversight of Audit and Assurance Processes
The board’s audit and sustainability committees should oversee financial and sustainability reporting and the processes for financial statements audit and sustainability assurance. ISA standard 700 requires the auditor to disclose key audit matters that arose during the financial audit.